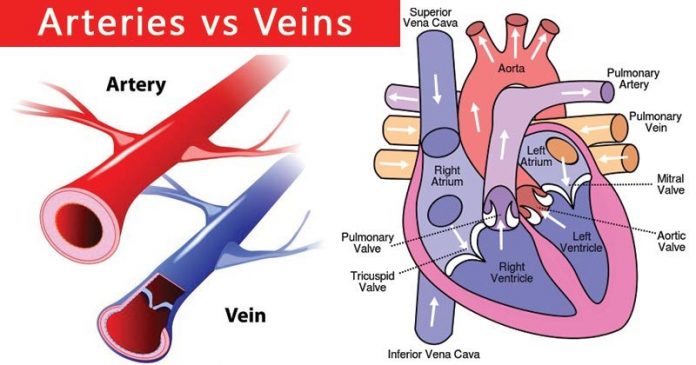
Blood used to transport various substances from one part of the body to another by flowing continuously around the body—the difference between arteries and veins. In invertebrates, blood flows through a closed system of blood vessels called the circulatory system.
This blood flow calls blood circulation. The blood keep circulating throughout the body using a muscular pump, the heart. When the heart relaxes, it fills up with blood, and when it contracts, the blood is squeezed out with great force. It then circulates through the blood vessels, which direct the blood flow around the body.
These blood vessels are arteries and veins.
What are arteries?
Arteries are blood vessels that carry the blood away from the heart. Since arteries receive blood directly from the heart, they must be able to withstand immense pressure. This pressure is due to the blood as it is forced out of the heart. Arteries have walls that are thick, elastic, and muscular. The strength of an artery to resist the pressure comes mainly from the elastic fibers. The elastic layer is much thicker in the great arteries near the heart.
The thick elastic walls help to maintain the high blood pressure in the artery. The elasticity permits stretching and recoiling of the artery wall—this helps to push the blood along.
The constriction and dilation of an artery are brought about by the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the arterial wall. therefore, When an artery constricts, its lumen becomes narrower and less blood flows through it in a given time. The paleness that one experiences at times are due to the constriction of arteries near the skin. On the other hand, when the artery dilates, its lumen becomes broader and more blood flows through it per unit.
What do you think has happened to the arteries when a person blushes? Do the arteries constrict or dilate?
What are veins?
The blood in the arteries is under tremendous pressure, but it is low when it reaches the veins. The blood flows more slowly and smoothly, so the walls of the veins need not be as thick and muscular as those of arteries. Hence, Veins also contain less elastic tissue. Instead, most veins have internal valves along their length to prevent the backflow of blood. These valves are folds of the inner walls, shape like half-moons. Hence they are called semilunar valves. The movement of blood along the vein is assisted by the action of skeleton muscles on the vein. Muscular exercise increases the pressure exerted on the veins and moves the blood along more quickly.
Are there any health risks involving arteries and veins?
If your veins or arteries get affected, then they might result in severe health issues. Some typical troubles faced by humans are:
Varicose veins: They are usually sited on the legs looking like veins swelling out of your skin. however, It usually happens when veins cannot send blood back to the heart as they do it usually. Varicose veins are primarily seen in overweight people; however, they are not very dangerous. People suffering from varicose veins feel soreness and pain in the affected area.
Artery plaque: Cholesterol and fatty materials together are known as plaque. The collection of plaque in arteries call atherosclerosis. Plaque built up inside the arteries weakens the blood flow in the body. It results in heart diseases, gangrene, or stroke.
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
Let’s have a look at how arteries and veins are different from each other. What characteristics do they have or are absent that make them distinct?
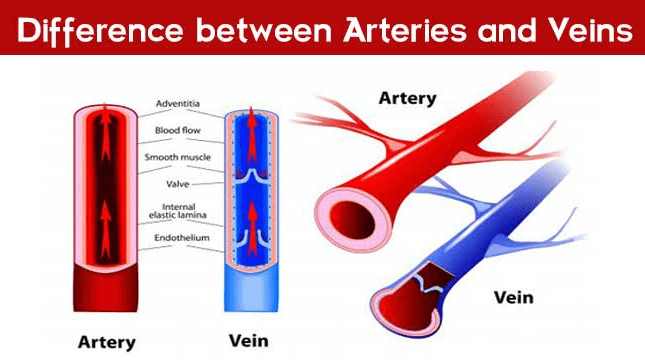
Arteries:
- These are blood vessels that carry the blood away from the heart.
- They are red as they carry oxygenated blood.
- These arteries are located deep inside the body.
- They carry red oxygenated blood except for pulmonary arteries. They carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Oxygen level is very high in arteries.
- Carbon dioxide level is low in arteries.
- the volume of blood is meager in arteries, as low as 15%
- It consists of three tissues: The outer coat (Tunica adventitia), The middle coat (Tunica media), and the inner coat (Tunica intima).
- The tunica adventitia is less developed in arteries.
- Tunica media is more muscular in arteries.
- The tunica intima is made up of endothelial cells that more elongate.
- Tunica media is the thickest layer of arteries.
- Arteries are more muscular and highly flexible than veins.
- The walls of arteries are very rigid and more robust than veins.
- Arteries consist of a narrow lumen that allows high blood pressure to flow through them.
- The movement of blood through arteries is spurt.
- The pulse of arteries is detectable.
- Arteries do not have valves except semilunar valves.
- The pathway of blood in arteries define and distinct.
- The vessels of arteries would remain open even if the blood flow stopped. It’s because of the thick muscular walls.
- The blood would start quirting if an artery injure.
- The muscles in arteries can contract.
- Arteries immediately empty up when a body dies.
- There are two types of arteries. Pulmonary arteries and systemic arteries.
- Some diseases associated with arteries’ problem are Atherosclerosis, Angina Pectoris, and Anthrogenesis- myocardial ischemia.
Veins:
- These are blood vessels that convey blood towards the heart
- These bluish-red as they carry deoxygenated blood.
- They are located near and beneath the surface of the skin.
- These carry bluish-red deoxygenated blood except for pulmonary veins. They carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
- Oxygen level relatively low compared to arterial blood.
- Carbon dioxide levels high in veins compared to arteries.
- The volume of blood in veins is as high as 65%.
- Veins have the same layers as arteries, but all three are thinner than arteries.
- It consists of three tissues: The outer coat (Tunica adventitia), The middle coat (Tunica media), and the inner coat (Tunica intima).
- Tunica adventitia is more developed in veins.
- The tunica media is less muscular in veins.
- The tunica intima made up of endothelial cells that less elongated.
- Tunica adventitia is the thickest layer of veins.
- Veins are less muscular and highly flexible than arteries.
- The walls of veins are significantly weaker and more collapsible than arteries.
- Veins consist of a wide lumen that reduces blood pressure flowing through them.
- The movement of blood through veins is sluggish.
- The pulse of veins is not detectable.
- Veins have valves, so the blood flows in the proper direction.
- The pathway of blood in veins not distinguished as they interconnect at many places.
- The vessels of veins will collapse if the blood flow stopped.
- The blood would start pooling if any vein injured.
- The muscles in veins are not able to contract.
- Veins fill up when a body dies.
- There are four types of veins. Hence, These are Deep veins, Superficial veins, Pulmonary veins, and Systemic veins.
- Some diseases that associate with the problem of veins are deep vein thrombosis and varicose veins.
The circulatory system is vital for human life. Interference or disruption in the heart or blood vessels can cause severe results and, sometimes, fatal.
Also read: Difference between speed and velocity.